Thin Film Solar (CIGS) vs. Monocrystalline Solar: Differences and Prospects
I. Thin Film Solar (CIGS)
With the growing global demand for green, renewable energy, the number of solar power plants is climbing rapidly. However, the efficiency and performance of solar power plants are affected by a variety of factors, of which meteorological conditions are one of the most critical. In order to ensure the stable and efficient operation of solar power plants, it is important to install a weather monitoring station (WMS).
1. Manufacturing process
Thin-film solar(CIGS)is a photovoltaic technology that utilizes thin films made of copper, indium, gallium, selenium and other elements as absorber materials. The first step in manufacturing CIGS thin-film solar cells is to prepare a CIGS absorber layer, usually by vacuum evaporation or sputtering. Next, a transparent conductive film and back electrode are added to the absorber layer to form a complete solar cell. This manufacturing process has the advantages of high production efficiency and low cost.
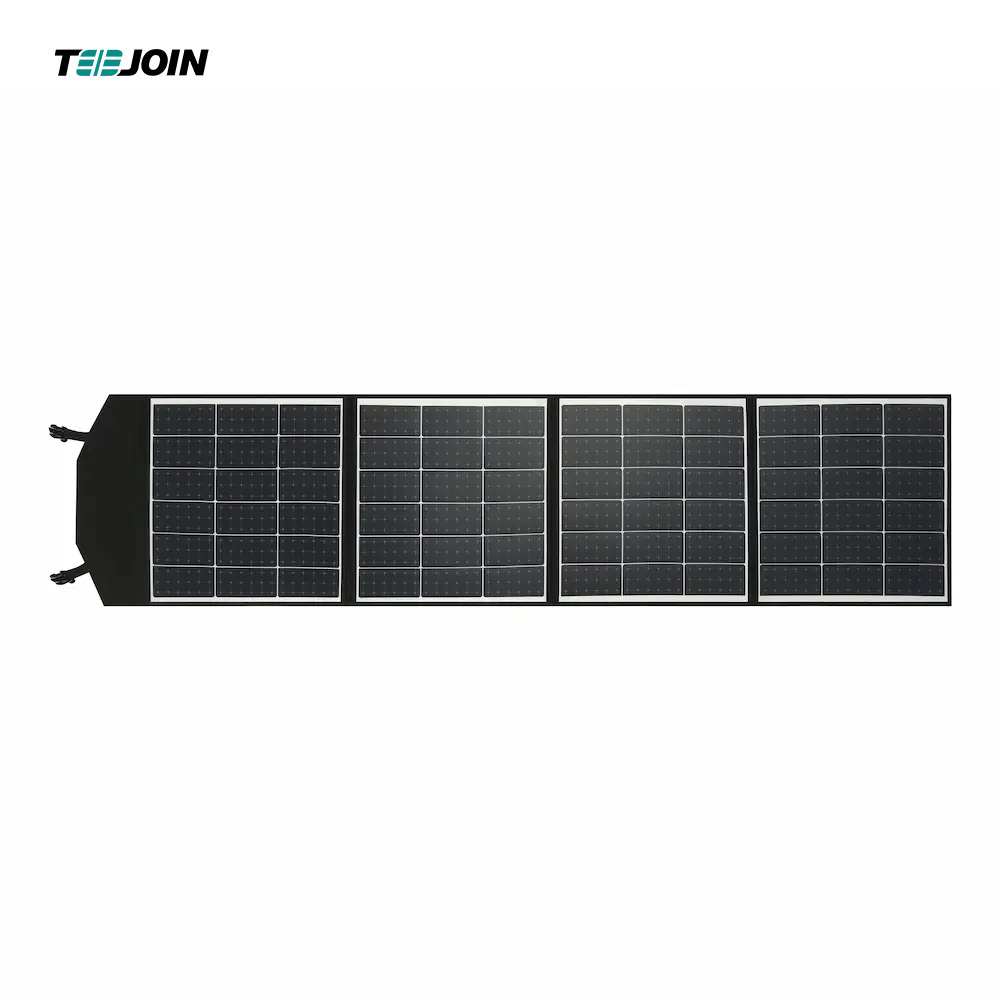

2. Performance Characteristics
CIGS thin film solar cells have high photoelectric conversion efficiency and good low light performance. In addition, the CIGS material system is flexible and adjustable, and the performance can be optimized by changing the elemental ratios. However, CIGS thinfilm solar cells have a shorter lifespan, are more expensive than commercially available products, and have the risk of environmental pollution, which are their main shortcomings.
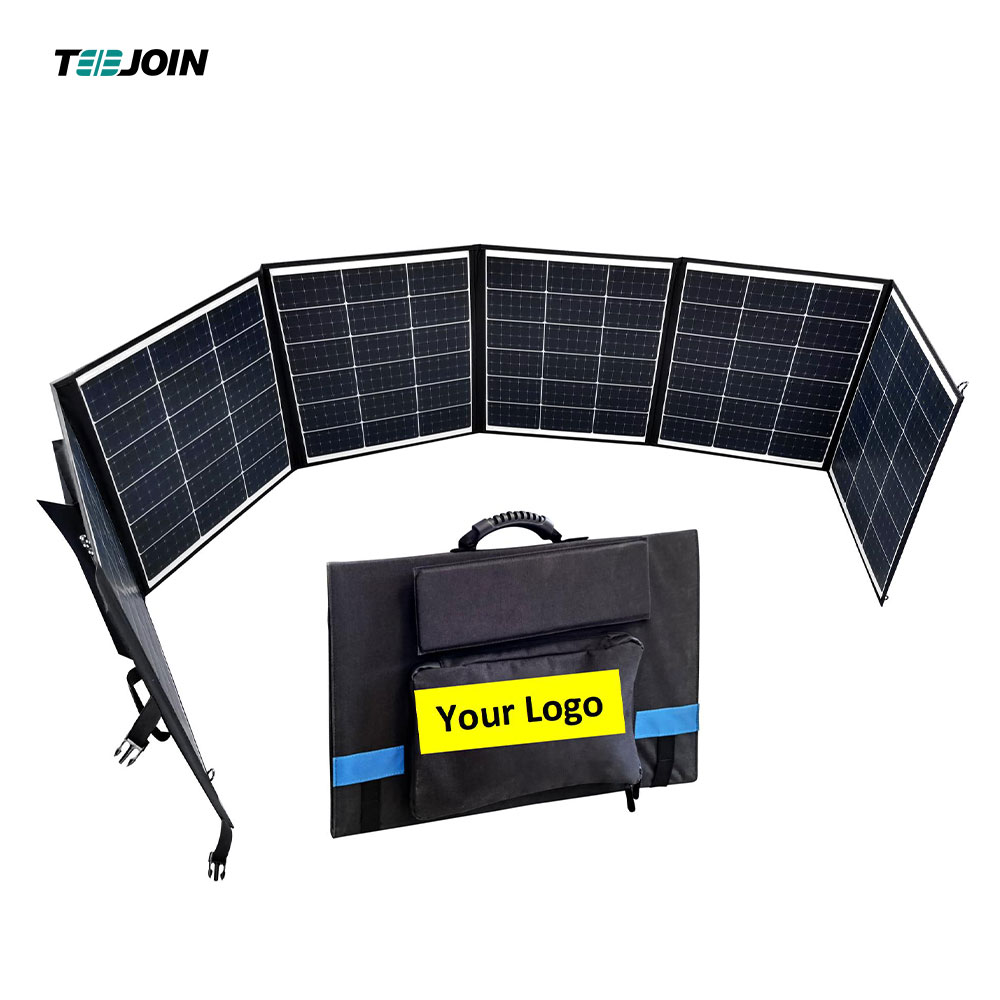

3. Application Areas
Because CIGS thin-film solar cells are thin, lightweight and bendable, they are suitable for the manufacture of solar modules for wearable devices, automobiles and buildings. In addition, CIGS technology can also be used to manufacture concentrated photovoltaic systems to improve photoelectric conversion efficiency.
II. Monocrystalline Silicon Solar
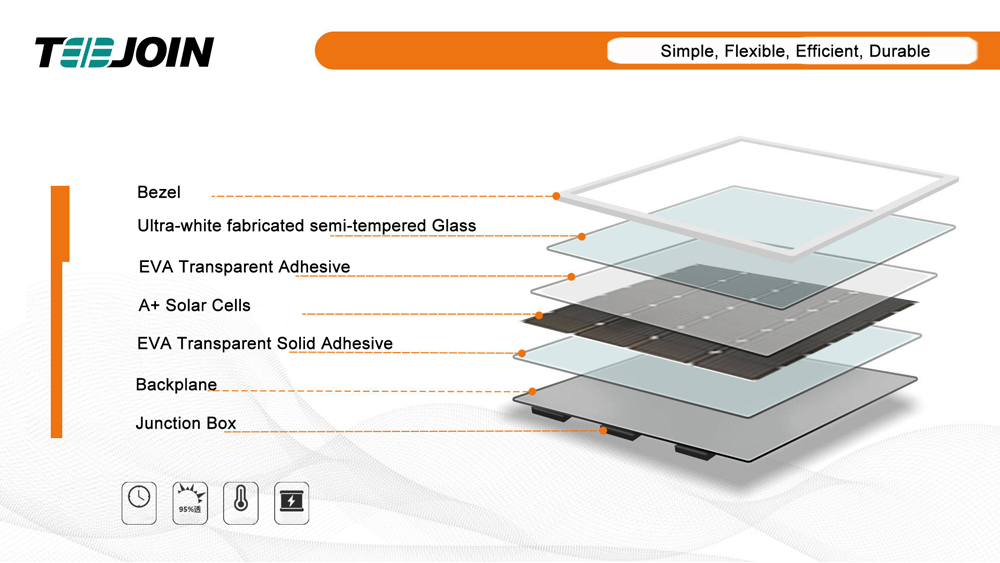
2.Performance Characteristics
Monocrystalline silicon solar cells have high photoelectric conversion efficiency and long life. Compared with CIGS thin-film solar cells, monocrystalline silicon solar cells have better stability and are suitable for a variety of harsh environments. In addition, monocrystalline silicon material system is mature and easy to prepare, so it has a certain advantage in terms of production cost. However, the manufacturing process of monocrystalline silicon solar cells produces a large amount of waste and pollution, which is its main shortcoming.
3. Application areas
Monocrystalline silicon solar cells are widely used in photovoltaic power plants, large-scale photovoltaic power plants and rooftop photovoltaics. Due to its high photoelectric conversion efficiency and long life, monocrystalline silicon solar cells have become one of the mainstream technologies in the photovoltaic industry. In addition, monocrystalline silicon solar cells can also be used to manufacture various shapes and sizes of photovoltaic modules to meet the needs of different application scenarios.

III. Development prospects
In the future development, the two technologies will compete with each other and learn from each other to achieve higher photoelectric conversion efficiency and lower cost.

Now on the market has appeared a lot of flexible solar panels made of monocrystalline silicon, the degree of bending has been comparable to CIGS, I believe that the use of monocrystalline silicon solar panels in the future will be more and more ahead of the curve.



